Routing :- Routing :- Routing is used for taking a packet from one
device and sending it through the network to another device on a different
network. The logical network address of the destination host is used to get
packets to a network through a routed network, then the hardware address of the
host is used to deliver the packet from a router to the correct destination
host.
· Destination
address
To be able to route packets, a router must know, at a minimum, the
following:
· Neighbour routers from which it can learn about remote networks
· Possible
routes to all remote networks
· The
best route to each remote network
· How
to maintain and verify routing information
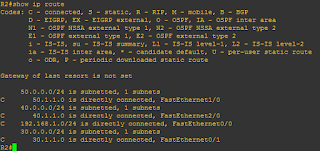
The router builds a routing table that describes how to find the
remote networks. If a network
is directly connected, then the router already knows how to get to
it. If a network isn’t
Connected, the router must learn how to get to the remote network
in two ways: by using static
Routing, meaning that someone must hand-type all network locations
into the routing table, or
Through something called dynamic routing.
The router builds a routing table that describes how to find the
remote networks. If a network
is directly connected, then the router already knows how to get to
it. If a network isn’t
Connected, the router must learn how to get to the remote network
in two ways: by using static
Routing, meaning that someone must hand-type all network locations
into the routing table, or
Through something called dynamic routing.
There are three types of
routing
1.
Static
2.
Default
3.
Dynamic

No comments:
Post a Comment